Paul Brear and Marko Hyvönen
Acta Crystallographica section F 78: 348-353 (2022)
DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X22008767
PDB coordinates:
7z39 (3D view)
Abstract
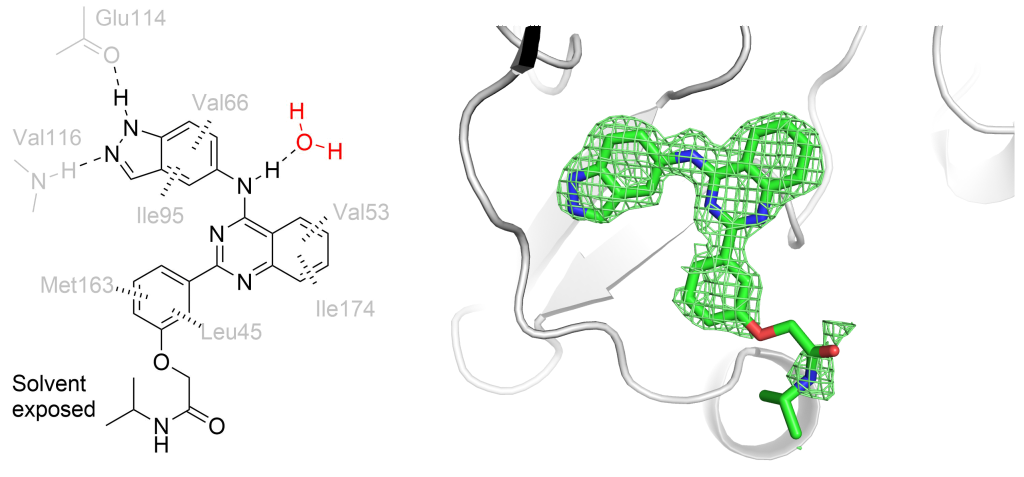
The small molecule belumosudil was initially identified as a selective inhibitor of Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase 2 (ROCK2) and has recently been approved for the treatment of graft-versus-host disease. However, recent studies have shown that many of the phenotypes displayed upon treatment with belumosudil were due to CK2α inhibition. CK2α is in itself a very promising therapeutic target for a range of conditions and has recently been put forward as a potential treatment for COVID-19. Belumosudil presents a promising starting point for the development of future CK2α inhibitors as it provides a safe, potent and orally bioavailable scaffold. Continue reading →