Alexander V Strizhak, Oleg Babii, Sergii Afonin, Iuliia Bakanovic, Teodors Pantelejevs, Wenshu Xu, Elaine Fowler, Rohan Eapen, Krishna Sharma, Maxim O Platonov, Vasyl V Hurmach, Laura Itzhaki, Marko Hyvönen, Anne S Ulrich, David R Spring, Igor V Komarov
Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 2020 May 11, Advance article in press
DOI: 10.1039/d0ob00831a
Pubmed: 32390036
PDB coordinates: 6y4q (3D view)
Abstract
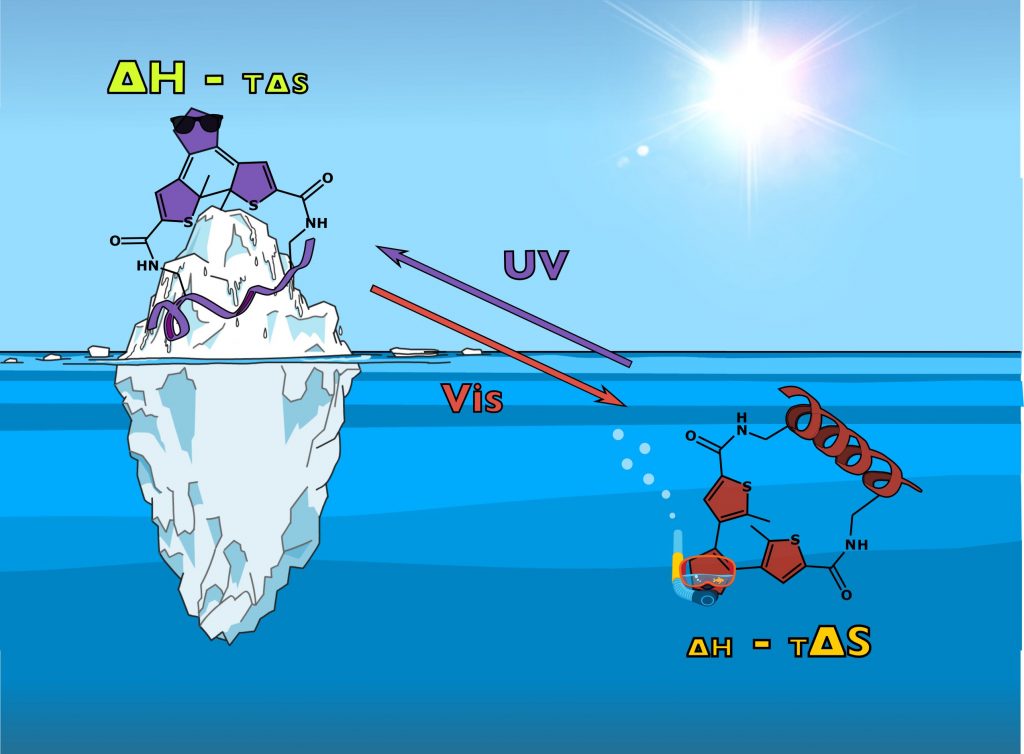
Analogs of the known inhibitor (peptide pDI) of the p53/MDM2 protein-protein interaction are reported, which are stapled by linkers bearing a photoisomerizable diarylethene moiety. The corresponding photoisomers possess significantly different affinities to the p53-interacting domain of the human MDM2. Apparent dissociation constants are in the picomolar-to-low nanomolar range for those isomers with diarylethene in the “open” configuration, but up to eight times larger for the corresponding “closed” isomers. Spectroscopic, structural, and computational studies showed that the stapling linkers of the peptides contribute to their binding. Continue reading →